The Possible Role of PD-1 Protein in Ganoderma lucidum–Mediated Immunomodulation and Cancer Treatment
Gan Wang, PhD1 , Le Wang, MS1, Jianlong Zhou, PhD2, and Xiaoxin Xu, PhD3
1Wayne State University, Detroit, MI, USA 2Longevity Valley Pharmaceuticals Co Ltd, Wuyi, Zhejiang Province, People’s Republic of China 3Lutuo Pharmaceuticals Inc, Jinan, Shandong Province, People’s Republic of China
Abstract
Background—Ganoderma lucidum has been used in Chinese medicine for thousands years to improve health and to promote longevity. One important function of G lucidum is to modulate the immune system. However, the underlying mechanism is not well understood. Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) is a cell surface protein present in certain immune cells (eg, B- and Tcells) and plays an important role in modulating the immune response. The role of PD-1 protein in G lucidum–mediated immunomodulation is unknown.
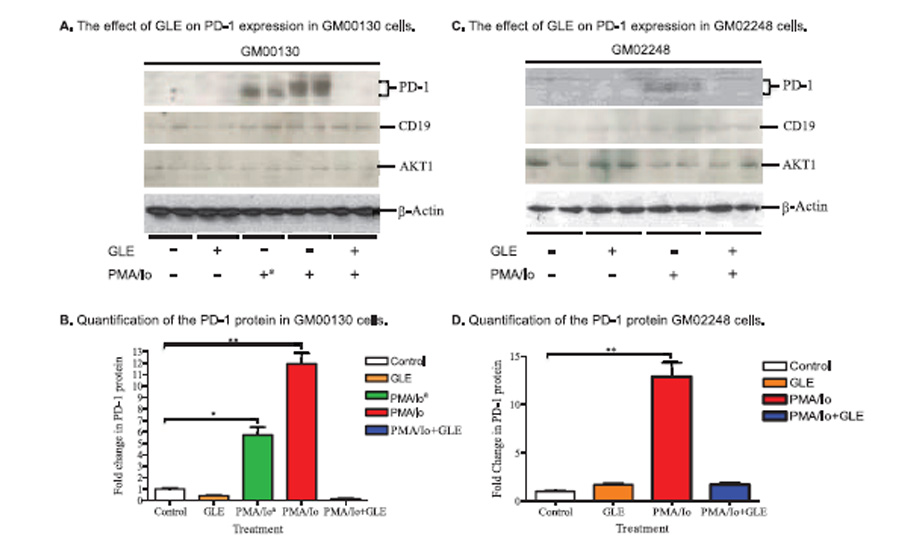
Results—Both our western blotting and IF staining results demonstrated great reduction in PD-1 protein and in proportion of PD-1+ cells in these B-lymphocytes. Our real-time PCR results indicated that this PD-1 protein
reduction was not caused by a transcriptional inhibition of the gene. In addition, our western blotting study further revealed that the GLE treatment caused an increase in expression of CCL5 chemokine in the cultured B-lymphocytes.
Conclusions—PD-1 protein is an important target of G lucidum–mediated immunomodulation. G lucidum and its
bioactive compounds can be developed into novel immunomodulators for prevention and treatment of cancer and
many other diseases.
Keywords
Ganoderma lucidum, Ganoderma lucidum spore extract, GLE, immunomodulation, PD-1, B-lymphocytes, protein reduction, transcription inhibition, novel immunomodulators (…)