Possible Mechanisms of Green Tea and Its Constituents against Cancer
Yohei Shirakami 1,2,* and Masahito Shimizu 1
1 Department of Gastroenterology, Gifu University Graduate School of Medicine, 1-1 Yanagido, Gifu 501-1194, Japan; shimim-gif@umin.ac.jp
2 Department of Informative Clinical Medicine, Gifu University Graduate School of Medicine, 1-1 Yanagido, Gifu 501-1194, Japan
* Correspondence: ys2443@gifu-u.ac.jp; Tel.: +81-58-230-630
Abstract
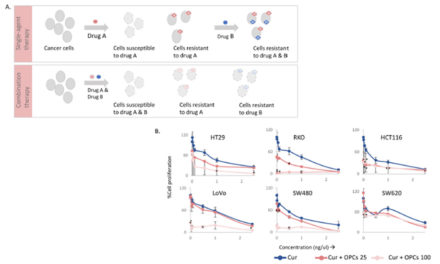
A number of epidemiological, clinical, and experimental researches have indicated that administration of green tea appears to have anti-cancer activity. According to findings of laboratory cell culture studies, a diverse mechanism has been observed underlying the effects of green tea catechins against cancer. These mechanisms include anti-oxidant activity, cell cycle regulation, receptor tyrosine kinase pathway inhibition, immune system modulation, and epigenetic modification control. This review discusses the results of these studies to provide more insight into the effects of green tea administration on cancers observed to date in this research field.
(…)
Keywords
catechin; green tea; cancer; chemoprevention; receptor tyrosine kinase2