Bacopa monnieri, a Neuroprotective Lead in Alzheimer
Disease: A Review on Its Properties, Mechanisms of
Action, and Preclinical and Clinical Studies
Aimi Syamima Abdul Manap1, Shantini Vijayabalan2, Priya
Madhavan3 , Yoke Yin Chia1, Aditya Arya3, Eng Hwa Wong3,
Farzana Rizwan3, Umesh Bindal3 and Shajan Koshy3
1School of Biosciences, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, Taylor’s University, Subang Jaya, Malaysia. 2School of Pharmacy, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, Taylor’s University, Subang Jaya, Malaysia. 3School of Medicine, Faculty of Health and Medical
Sciences, Taylor’s University, Subang Jaya, Malaysia.
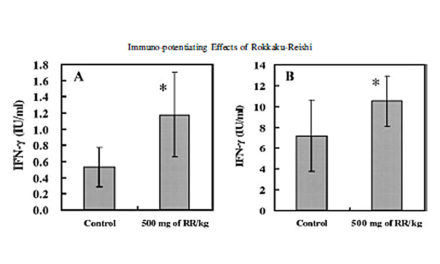
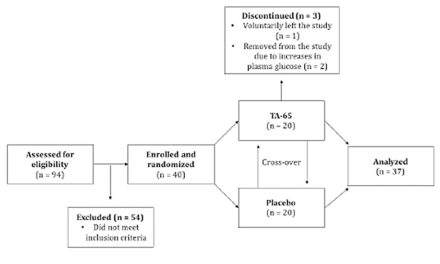
ABSTRACT: Alzheimer disease is a neurodegenerative disease that is signified by cognitive decline, memory loss, and erratic behavior. Till date, no cure for Alzheimer exists and the current Alzheimer medications have limited effectiveness. However, herbal medicines may slow down the disease’s progression, which may hopefully reduce the number of cases in the years to come. Numerous studies have been done on characterizing the neuroprotective properties from plants belonging to Scrophulariaceae family, particularly Bacopa monnieri and its polyphenolic compounds known as bacosides. This review presents the findings on bacosides in therapeutic plants and their impact on Alzheimer disease pathology. These reports present data on the clinical, cellular activities, phytochemistry, and biological applications that may be used in new drug treatment for Alzheimer disease.
Keywords: Alzheimer, aging, therapeutic plant, Bacopa monnieri, bacoside